What is an adverb? How does an adverb modify different parts of speech? What rules are applied to form an adverb? This article will define and explain the adverb and their different types and their uses in sentences.
Definition of Adverb with Examples
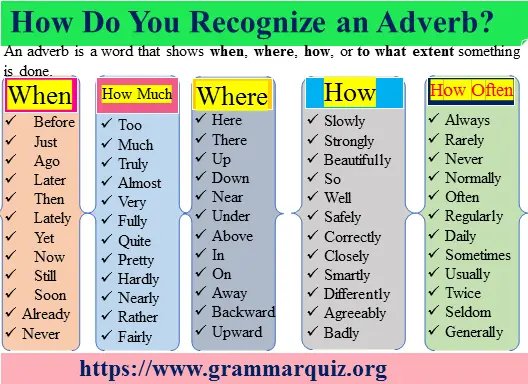
A modifying word used to describe a verb, an adjective, another adverb, or a whole phrase is called an adverb. It functions most commonly as a verb modifier that shows when, where, how, or to what extent something is done. Read the following sentences and note how adverbs describe different parts of speech.
What Are Examples of Adverbs?
Examples of Adverbs Modifying Verbs
- He threw the stones carelessly in different directions.
- They live together peacefully.
- He studied hard last night.
- It is raining heavily.
- The parrots are singing sweetly.
Related: Position of Adverb in Sentences
Examples of Adverbs Modify Adjectives
- She is extremely beautiful.
- He was unusually intelligent.
- His brother was seriously injured in an accident.
- She is a really nice girl.
- He is fairly clever with computers.
Examples of Adverbs Modify Another Adverb
- She learns lessons incredibly quickly.
- He was treated very badly.
- He knows pretty well everything.
- He is undoubtedly very intelligent.
Examples of Adverbs Qualify Participles
- I am greatly pleased.
- She looks rather confused.
- He is mostly honored to meet her brother.
Examples of Adverbs Modify a Whole Sentence
- Obviously, he was not in the mood.
- Certainly, she is wrong.
8 Types of Adverbs with Examples
In the following sentences, you will notice adverbs can do many different functions in a sentence.

- She went very fast.
- We pay our house rent monthly.
- I have seen him twice.
- She played the piano well.
- I searched for her bag everywhere.
- He lives in a very hilly area. He is leaving tomorrow.
Based on these and several other functions’ adverbs are classified into eight types.
Types of Adverbs (Adverbs of Time Definition & Examples)
Adverbs of time give information about time. It answers the question of when something happens, or has happened or will happen.
Adverb of Time Examples
- I haven’t seen any good films recently.
- I am studying now.
- He has just arrived.
- Ahmad is always cheerful.
- He has already graduated.
- They haven’t come yet.
- We met each other last year.
- I will graduate this year.
- She left the house over half an hour ago.
- I have not met her since.
- It’s raining again.
- We may finish it tomorrow.
- The weather is cold this evening.
List of Adverbs of Time
- Before
- Just
- Ago
- Later
- Recently
- Then
- This year
- Next year
- Last night
- Lately
- Yet
- Now
- Still
- Soon
- Later
- Yesterday
- Already
- Never
- Afterwards
- Eventually
Types of Adverbs (Adverbs of Frequency Definition & Examples)
Adverbs of frequency show how often we do something. It gives more information about an action that happened all the time, many times, a few times, or the action does not happen at all.
Commonly used adverbs of frequency are
always, regularly, occasionally, usually, normally, generally, sometimes, often, rarely, seldom, hardly ever, never, daily, weekly, monthly, etc.
Adverbs of Frequency Examples
- She always comes late.
- He rarely visits his parents.
- He has never been to London.
- She normally gets up at five o’clock.
- We often see each other in the garden.
- I see her occasionally in college.
- We meet our supervisor daily.
- I sometimes play the piano.
- We usually spend the holiday abroad.
- I have warned him twice.
Some of these adverbs describe the action indefinitely.
In addition to the adverbs mentioned above, there are several expressions called the expression of frequency used to express how often we do an activity. Examples of such expressions are given below.
Once or twice a day/week/month etc.
Once in a while.
Most of the time.
From time to time (means Occasionally.)
These expressions answer the question of how often something happens. They usually come at the start or the end of a sentence but do not come in the middle.
Examples
- The post comes twice a week.
- Once in a while, she phoned him.
- Most of the time, he gets home about 7 o’clock.
Adverbs of Place (Definition & Examples)
Adverbs of place describe where something happens, happened, or will happen. They give information about direction, movement, or distance, etc. The following words are adverbs of place.
here, there, everywhere, somewhere, up, down, near, under, above, in, on, away, backward, upward, behind, across, above, outside, inside, off, etc.
Adverbs of Place Examples
- It’s stopped raining. Let’s go outside.
- The smoke spread everywhere.
- We may find him here.
- She is walking inside.
- Go there.
- Come in.
- She is watching a film upstairs.
- I will go abroad to study.
The following adverbs ending in -ward describe directions.
e.g., downward, forward, onward, upward, backward, outward, inward.
- The car keeps moving forwards / forward.
- They go onwards in a northerly direction.
- She walked backwards towards the car.
- The window opens outwards.
Adverbs of Manner (Definition & Examples)
Adverbs of manner show how something happened or will happen. Adverbs of manner are usually formed from adjectives. Adverbs of manner usually come at the end of a sentence. It may also come in the middle of a sentence.
The words slowly, strongly, beautifully, so, well, etc., are adverbs of manner.
Examples of Adverb of Manner
- They arrived safely.
- He has answered all questions correctly.
- I am working closely with them.
- She was smartly dressed.
- Every student was treated differently.
- He performed wonderfully in the game.
- The essay was well written.
- I was agreeably surprised by the price.
Adverbs of Degree (Definition & Examples)
Adverbs of degree describe to what extent something happens or will happen. They describe the intensity or degree of a verb, an adjective, or another adverb they are qualifying. In other words, adverbs of degree strengthen or weaken the original meaning of the verb, adjective, or adverb. Examples of adverbs of degree are
completely, undoubtedly, too, much, truly, almost, very, fully, quite, pretty, hardly, extremely, nearly, rather, somewhat, fairly, etc.
Adverbs of Degree Examples
- He works rather fast.
- The wrestler was very strong.
- He was undoubtedly the best teacher.
- He was extremely intelligent.
- I almost finished my homework.
- It’s too hard for me to explain.
- She drinks much water.
Interrogative Adverbs (Definition & Examples)
Interrogative adverbs are the question words that help us identify the time, location, or manner of action. Common interrogative adverbs are given below.
When (Identify time)
Where (Identity location)
How (Identify manner)
Why (Identify reason)
how soon, how late, how often, how near, how long ago, how far, etc.
Examples
- How did you get to his home?
- When did he arrive?
- How long ago did your father died?
- How far can you walk?
- Why did you join their party?
Relative Adverbs (Definition & Examples)
An adverb that introduces relative or adjective clauses is called relative adverbs. When, how, where, why are relative adverbs. We use these adverbs to give information that relates to place, time, reason
Examples
- The man who I met was my fellow.
- They asked me why I didn’t attend the party.
- It all depends on how you treat him.
Adverb of Affirmation and Negation (Definition & Examples)
Certainly, not, yes, yea, apparently, verily, obviously, no, undoubtedly, obviously, of course, perhaps, indeed, etc.
- Can you give me your number? No.
- It is never true.
- Will he go with us? Certainly.
- Perhaps he has not yet reached his house.
Formation of Adverbs (Rules & Examples)

Formation of adverbs: Most adverbs are formed from adjectives by adding -ly.
| Adjective | Adverb |
| Slow | Slowly |
| Quick | Quickly |
| Hard | Hardly |
| Loud | Loudly |
| Soft | Softly |
| Warm | Warmly |
| Wide | Widely |
Some adjectives end in “-y” to form adverbs from such adjectives left out the “-y” and add “-ily.”
| Easy | Easily |
| Happy | Happily |
| Pretty | Prettily |
| Angry | Angrily |
| Tidy | Tidily |
| Heavy | Heavily |
If an adjective end in -le or -ue drop the e and add -y
| Simple | Simply |
| Nice | Nicely |
| Gentle | Gently |
| Terrible | Terribly |
| Horrible | Horribly |
| Due | Duly |
| True | Truly |
Adjectives end in -l take -ly to form an adverb.
| Awful | Awfully |
| Careful | Carefully |
| Beautiful | Beautiful |
| Wonderful | Wonderfully |
| Usual | Usually |
| Physical | Physically |
| Logical | Logically |
Adjective end in -ic usually take -ally or -ly to form adverb
| Tragic | Tragically |
| Public | Publicly |
| Drastic | Drastically |
| Enthusiastic | Enthusiastically |
| Scientific | Scientifically |
Not all adverbs end in -ly. Some adjective ends in -ly. Too.
e.g., Lovely, elderly, silly, lonely, lively, friendly, ugly
The following adverbs have the same form as adjectives.
- Fast
- Well
- Hard
- Late
- Early
- kindly
- High/Highly
- Much/more/most
- Enough
- Back
- Far
- Fast
- Ill
- Still
Examples
Adjective: The field is still hard.
Adverb: She failed her exam because she didn’t study very hard.
Adjective: He is a fast swimmer.
Adverb: He drives his car fast.
Adjective: I got four answers right.
Adverb: He called right after dinner.
The adverb well can also be used as an adjective.
- She hasn’t been too well lately. (means healthy)
- He was not present at school yesterday. I think he is not well. (means healthy)
Some adverbs are formed by adding different prefixes and suffices. For example
- Sideways form side
- always from all
- lengthways from length
- Backward from back
- upwards from up
- downward from down
- inwards from in
- homewards from home
- Crosswise from cross
- contrarywise from contrary
- Abreast from breast
- anew from new
- ashore from shore
- aside from side
A few adverbs are formed by adding -wise to nouns or prepositions:
E.g., clockwise, anti-clockwise, counter-clockwise, crosswise, lengthwise