Second Conditional Definition and Examples
The second conditional sentences, also called the unreal conditional, takes the past simple tense in the if clause followed by a conditional tense in the main clause.
Must Learn: 10 Examples of Second Conditional
- If I had money, I would lend it to you. (But I haven’t money)
- If her brother gave her the money, she would go on holiday.
- The company would probably promote him if he worked harder.
- If I went there, I would meet his brother.
- If she didn’t call, I wouldn’t recognize her.

The past tense expresses unreal or improbable things. It isn’t a true past but a subjunctive.
Structure of Second Conditional Sentences
The second conditional is introduced by the if clause with a verb in the simple past tense. The model verbs Would, could, or might, and the base form of the verb describes the result.
Related: Third Conditional- Structure, Uses with Examples Sentences
If + past simple, + would/could/might + base form of verb
OR If + past continuous/past perfect, + would/could/might + base form of verb
“Would” in the second conditional describe something we would definitely do. We can also use “could” for what we would be able or allowed to do. Might describe things that are possible (but unlikely) we would do.
Second Conditional Sentence Examples
- If we went to the United States, we would visit San Francisco. (certain result)
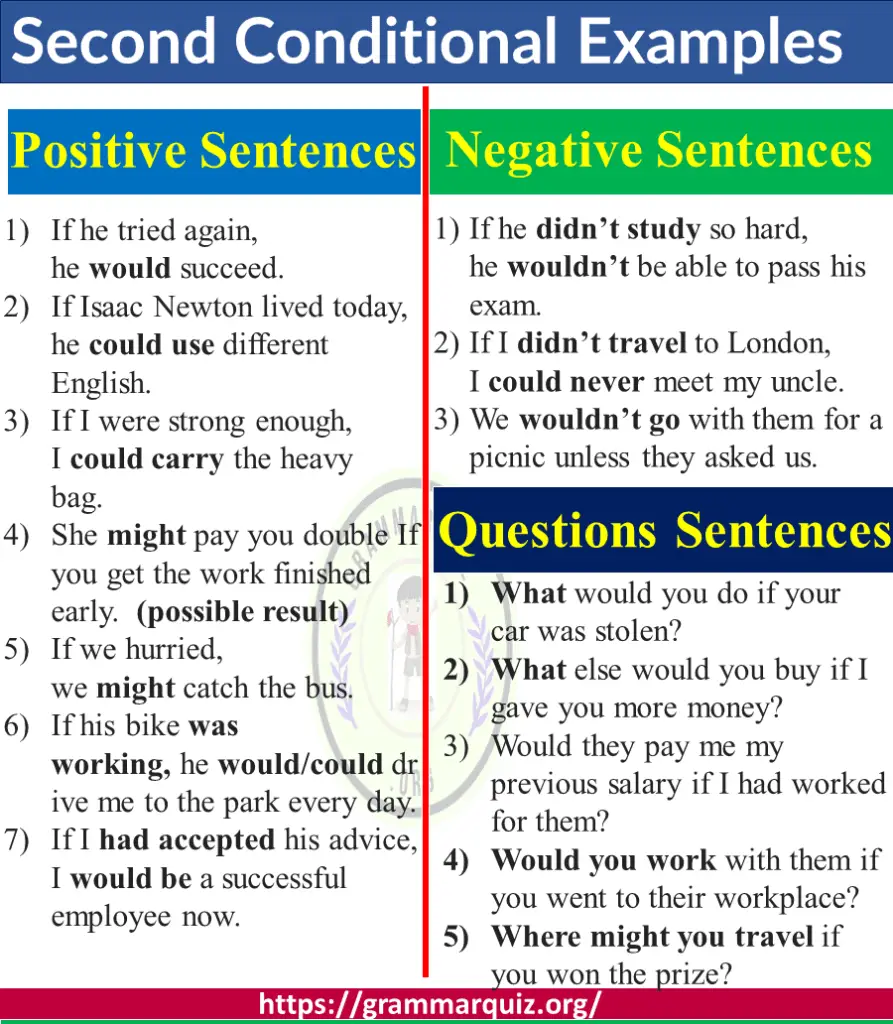
- If he tried again, he would succeed.
- If Isaac Newton lived today, he could use different English.
- If I were strong enough, I could carry the heavy bag. (Express ability)
- She might pay you double If you get the work finished early. (possible result)
- If we hurried, we might catch the bus.
- If his bike was working, he would/could drive me to the park every day.
- If I had accepted his advice, I would be a successful employee now.
- If they were invited, of course, they would come.
Second Conditional Negative Sentences with Examples
The second conditional sentence can also be used in negative form to describe a situation that would not happen if something else were also not to happen. For the formation of negative in the second conditional, we put the simple past tense in the if-clause in its negative form as well as make would or could or might negative in the main clause.
Examples
- If he didn’t study so hard, he wouldn’t be able to pass his exam.
- If I didn’t travel to London, I could never meet my uncle.
- We wouldn’t go with them for a picnic unless they asked us.
Second Conditional Questions Sentences with Examples
To form questions in the second conditional invert would, could, or might with the subject. We can also form questions in the second conditional using question words such as what, where, and who, etc., by putting them in front of would.
Examples
- What would you do if your car was stolen?
- What else would you buy if I gave you more money?
- Would they pay me my previous salary if I had worked for them?
- Would you work with them if you went to their workplace?
- Where might you travel if you won the prize?
When to Use the Second Conditional?
The second conditional is used in a situation when something does not have a real possibility of happening; we just imagine the result of an unlikely situation in the present or future. For example, a boy says
- If I found some money somewhere in the school, I would take it to the headmaster’s office.
In this example, the boy just imagines the situation and doesn’t expect to find some money somewhere in the school.
The second conditional is also used when we talk about a situation that is contrary to a known situation.
Second Conditional Usage Examples
- If I lived near your house, I would be happy. (But I don’t live near your house.)
- If I were you, I would ride the bike all day.
Note that the use of “were” with the third person singular he, she, it, and singular nouns in the if-clause, because it is considered the most appropriate form instead of using, was with these pronouns.
The second conditional is also used to describe actions that we do not expect to happen.
Examples
- If a thief entered my home at night, I would scream. (But I don’t expect a thief to enter in.)
- If I wore these clothes, everyone would laugh at me. (But I don’t intend to wear it.)
- I would buy a new car if I found a million dollars. (I don’t expect this to happen)
- If I were there, I would tell him what to do.
Related:
- Zero Conditional Sentences
- First Conditional Sentences
- Third Conditional Sentences
- Mixed Conditional Sentences