The word gender in English is taken from Latin (genus), which means kind or class. In the English language, the gender grammatical distinction corresponds with the natural difference of sex. Many languages around the world use gender. Gender in a language is just a way of classifying nouns into classes. They may refer to male or female. To decide which personal pronoun and which possessive determiner should be used instead of the noun going before the gender differentiation in such cases is relevant. For example
- She found her phone.
- She had been looking for it.
- Here is her bag; take it away.
- I think she had been looking for it.
All nouns in English fall into four gender groups.
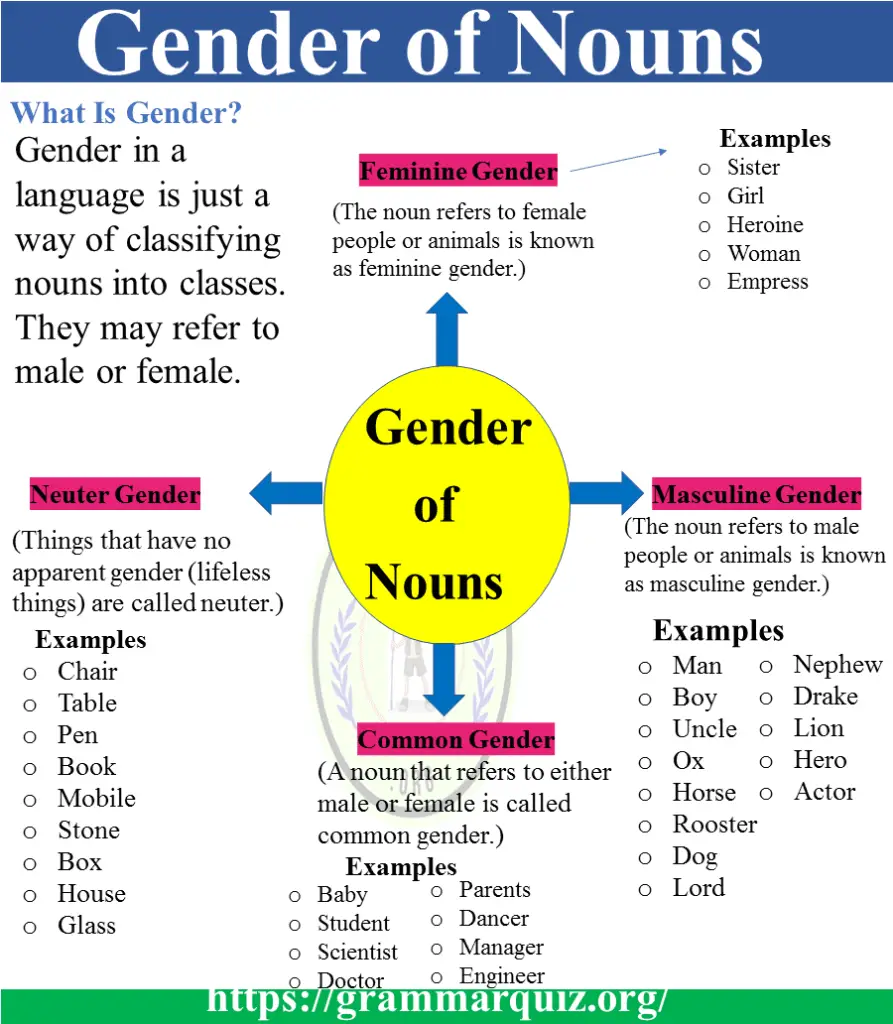
What is Masculine Gender? Definition and Examples
The noun refers to male people or animals is known as masculine gender. We use them with the pronouns he, his, him.
Father, boy, bull, man, Mr. David, etc., are nouns of masculine gender.
What is Feminine Gender? Definition and Examples
The noun refers to female people or animals is known as feminine gender. We use them with the pronouns she, her, hers.
Sister, girl, heroine, woman, empress, etc., are nouns of feminine gender.
The Neuter Gender Nouns Definition and Examples
Things that have no apparent gender (lifeless things) are called neuter. In some exceptional cases, we associate the neuter gender with children and small animals. For example
- My son loves his little cat and cannot do without it.
- I saw a black dog. It was running across the road.
- The horse fell and broke its leg.
- When we saw the baby, it was crying.
Nouns refer to abstract notions, and inanimate objects also fall in the category of neuter gender.
Examples of Nouns of neuter gender are
- Chair
- Table
- Pen
- Book
- Mobile
- Stone
- Box
- House
- Glass
The Common Gender Nouns
A noun that refers to either male or female is called common gender.
Examples of Common gender are
- Baby
- Student
- Scientist
- Doctor
- Parents
- Dancer
- Manager
- Engineer
- Singer
- Friend
- Speaker
- Rider
- Reporter
- Cousin
- Journalist
Rules of Forming the Feminine from Masculine Gender
We can distinguish the genders of nouns using three ways.
Firstly, we are employing an entirely different word to form the feminine.
| Masculine | Feminine |
| Man | Woman |
| Boy | Girl |
| Boar | Sow |
| Husband | Wife |
| King | Queen |
| Uncle | Aunt |
| Wizard | Witch |
| Son | Daughter |
| Brother | Sister |
| Father | Mother |
| Colt | Filly |
| Hero | Heroine |
| Tutor | Governess |
| Bull | Cow |
| Dog | Bitch |
| Monk | Nun |
| Mallard | Wild Duck |
| Horse or stallion | Mare |
| Bachelor | Spinster |
| Youth | Maiden |
| Lad | Lass |
| Buck | Doe |
| Fox | Vixen |
| Gander | Goose |
| Drake | Duck |
| Tomcat | Tabby Cat |
| Lord | Lady |
| Lad | Lass |
| Nephew | Niece |
| Widower | Widow |
| Bride-groom | Bride |
| Sir | Madam |
| Papa | Mama |
| Ram | Ewe |
| Rooster | Hen |
| Bullock or steer | Heifer |
| Mr. | Mrs. |
| Tailor | Dressmaker |
| Gentleman | Lady |
| Sultan | Sultana |
| Signor | Signora |
Forming Feminine Gender Using Suffixes
In a second way, the suffix “-ess,” “ix,” “en,” “in” is added to the masculine gender to form its feminine.
| Masculine | Feminine |
| Abbot | Abbess |
| Author | Authoress |
| Actor | Actress |
| Hunter | Huntress |
| Poet | Poetess |
| God | Goddess |
| Governor | Governess |
| Founder | Foundress |
| Instructor | Instructress |
| Giant | Giantess |
| Prince | Princess |
| Peer | Peeress |
| Priest | Priestess |
| Prophet | Prophetess |
| Protector | Protectress |
| Patron | Patroness |
| Conductor | Conductress |
| Tiger | Tigress |
| Host | Hostess |
| Shepherd | Shepherdess |
| Sorcerer | Sorceress |
| Songster | Songstress |
| Director | Directress |
| Dauphin | Dauphiness |
| Deacon | Deaconess |
| Manager | Manageress |
| Master | Mistress |
| Waiter | Waitress |
| Emperor | Empress |
| Steward | Stewardess |
| Lion | Lioness |
| Duke | Duchess |
| Count | Countess |
| Marquess | Marchioness |
| Mayor | Mayoress |
| Negro | negress |
| Baron | Baroness |
| Ambassador | Ambassadress |
| Murderer | Murderess |
| Benefactor | Benefactress |
By placing a feminine word before or after a masculine
| Masculine | Feminine |
| Grandfather | Grandmother |
| Boy cousin | Girl cousin |
| Boyfriend | Girlfriend |
| Manservant | Woman servant |
| Milkman | Milkmaid |
| Landlord | Landlady |
The sun, time, winter, summer, dawn, morn, and death are made masculine. The moon, the earth, the night is feminine.