12 Types of English Tenses
12 Types of English Tense! To learn and understand the concept of tenses, first, we need to understand verbs and their form.
To learn and understand the concept of tenses, first, we need to understand verbs and their form. Verb: Words that express states or actions is called a verb. The words written in bold are verbs in the below sentences. It shows what someone did in the past, is doing right now, or how someone or something is.
- I walk five kilometers to school every day.
- The sun melted the ice.
- She was singing last night.
- A book lay on the table.
- He is a funny person.
- It was not an excellent time.
Learn: English Verbs Definition and Types with Examples
Forms of a Verb
There are four principal forms of verbs.
The Infinitive- The first form of a verb is called the present or base form. The first form of a verb is used to form the present tense. e.g., to sing, to play, to be, to work
The Past- The second form of a verb is called the past form. This form of a verb is used to make the past tense.
Played, wrote, went, got, etc.
The Past Participle- The third form of a verb is called the past participle and is used to form perfect tenses.
Gone, written, been (to be), played, etc.
The Present Participle- The fourth form of a verb is called the present participle. It is also called the continuous, progressive, or ing form. This form of a verb is formed when we add -ing to the infinitive or present form of a verb. We form continuous tenses using this form of a verb.
The verbs in the following sentences introduce three times.
- I visit this school twice a month.
- I last visited this school yesterday.
- I will visit this school tomorrow.
In the first sentence, the verb visit refers to the present time.
The verb visited in the second sentence refers to past time.
The verb will visit in the last sentence refers to future time.
Definition of Tense
A tense is a form of the verb which shows when an action happened (gives information about time) and the state of an action (the action is completed, is in progress, or will be completed in the future). Thus, tense provides information about time and state.
Time and aspects: There are technically three times. The Present, past, and future and four aspects are simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. The time and aspects combine and make all twelve tenses.
e.g.
1- The present time and the simple aspect combine and make the present simple tense.
2- The past time and simple aspect combine and make the simple past tense.
3- The future time and simple aspect combine and make simple future tense.
Look at the table below.
| Simple | Continuous | Perfect | Perfect Continuous | |
| Present | Present Simple | Present Continuous | Present Perfect | Present Perfect Continuous |
| Past | Past simple | Past Continuous | Past Perfect | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Future | Future Simple | Past Continuous | Past Perfect | Past Perfect Continuous |
Formation of Tenses
Formation refers to combining specific words in a particular order to form a tense. These particular words are subject, verb, and object. The form of a verb is changed according to the tense.
Study the following sentences and note the form of the verb in different tenses.
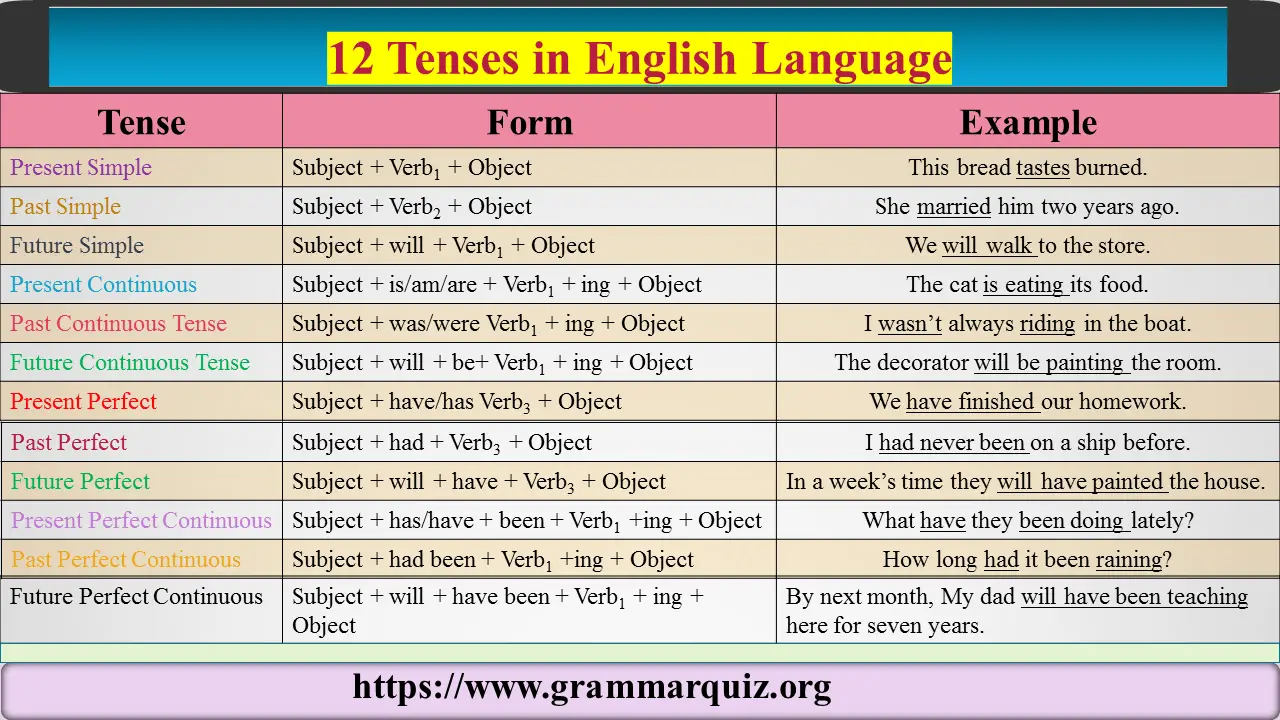
Present Simple Tense
Form: Subject + Verb1 + Object
Examples
- I carry the bag.
- You carry the bag.
- He/she carries the bag.
- We carry the bag.
- They carry the bag.
Present Continuous Tense
Form: Subject + is/am/are Verb1 + ing + Object
Examples
- I am carrying the bag.
- You are carrying the bag.
- He/she is carrying the bag.
- We are carrying the bag.
- They are carrying the bag.
Past Simple Tense
From: Subject + Verb2 + Object
Examples
- I took him to the wedding.
- You took him to the wedding.
- He/she took him to the wedding.
- We took him to the wedding.
- They took him to the wedding.
Past Continuous Tense
Form: Subject + was/were Verb1 + ing + Object
Examples
- I was reading the newspaper.
- You were reading the newspaper.
- He/she was reading the newspaper.
- We were reading the newspaper.
- They were reading the newspaper.
Present Perfect Tense
Form: Subject + have/has Verb3 + Object
Examples
- I have rushed.
- You have rushed.
- He/she has rushed.
- We have rushed.
- They have rushed.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Form: Subject + has been/have been + Verb +ing + Object
Examples
- I have been rushing.
- You have been rushing.
- He/she has been rushing.
- We have been rushing.
- They have been rushing.
Past Perfect Tense
Form: Subject + had + Verb3 + Object
Examples
- I had finished studied.
- You had finished study.
- He/she had finished study.
- We had finished study.
- They had finished study.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Form: Subject + had been + Verb +ing + Object
Examples
- I had been finishing study.
- You had been finishing study.
- He/she had been finishing study.
- We had been finishing study.
- They had been finishing study.
Future Simple Tense
Form: Subject + will + Verb1 + Object
Examples
- I will cry
- You will cry
- He/she will cry
- We will cry
- They will cry
Future Continuous Tense
Form: Subject + will + be+ Verb1 + ing + Object
Examples
- I will be crying
- You will be crying
- He/she will be crying
- We will be crying
- They will be crying
Future Perfect Tense
Form: Subject + will + have + Verb3 + Object
Examples
- I will have played
- You will have played
- He/she will have played
- We will have played
- They will have played
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Form: Subject + will + have been + Verb1 + ing + Object
Examples
- I will have been playing.
- You will have been playing.
- He/she will have been playing.
- We will have been playing.
- They will have been playing.
Similarities Between Different English Tenses
There are some similarities between different English tenses. For example, all continuous tenses take continuous form or present participle of the main verb—the auxiliary verb going before the main verb form the actual tense. For example
Present Continuous: The doctor is seeing patients for most of the morning.
Past Continuous: She was singing loudly in the room.
Present Perfect Continuous: The dog has been frightening the baby again.
Past Perfect Continuous: The birds had been singing on the tress.
Future Perfect Continuous: She will have been washing the clothes all day when we reach.
Similarly, all perfect tenses take the third form of the main verb. The auxiliary verb before the main verb determines which tense it is. For example
Present Perfect: I have eaten dinner at about 7 o’clock.
Past Perfect: She had worked in this company for many years before she got the promotion.
Future Perfect: I will have finished my homework when I come to school tomorrow.