Present Continuous Tense Structure with Examples
We make the present continuous tense with the continuous form, also known as the -ing form of the main verb after the auxiliary verb is, am, and are.
Must Learn: Past Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense Positive Sentences with Examples
Structure: Subject + is/am/are (Verb1) +ing + Object
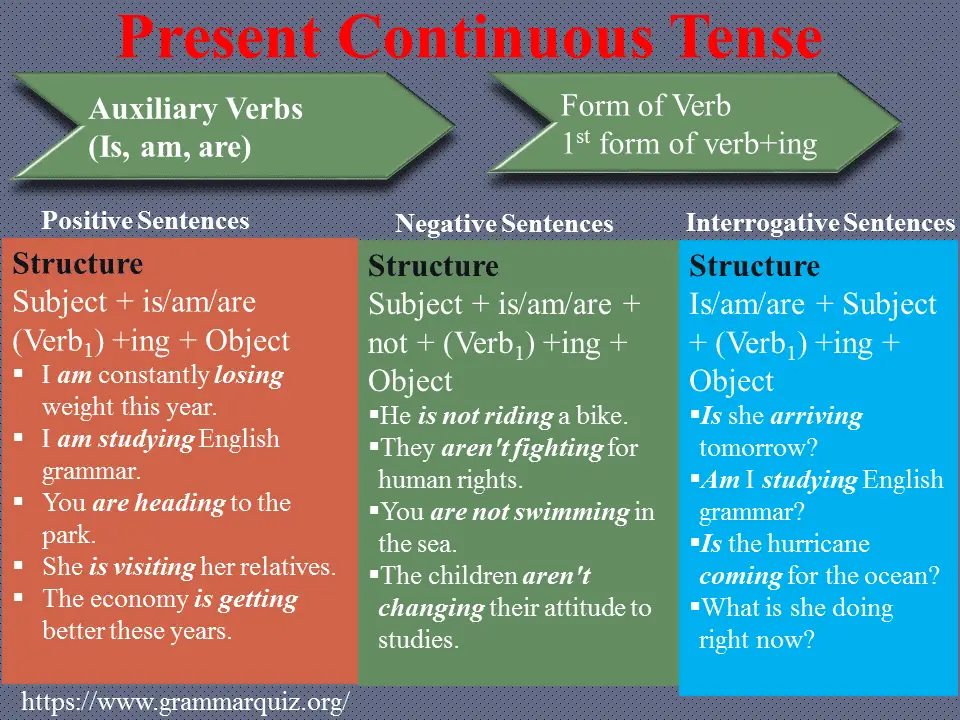
Present Continuous Tense Positive Sentences Examples
- I am constantly losing weight this year.
- The baby is getting better.
- She is visiting her relatives.
- Ali is sleeping with the window open tonight.
- I am studying English grammar.
- You are heading to the park.
- They are playing cricket.
- The economy is getting better these years.
- She is losing her precious time at this job.
- This man is always finding fault with the machine.
Present Continuous Tense Negative Sentences with Examples
The present continuous negative is formed by inserting the word not between the “be verb” and the main verb. It describes what is not currently happening. The auxiliary verbs ‘is and am are often contracted with not as ‘isn’t and aren’t.
Structure: Subject + is/am/are + not + (Verb1) +ing + Object
Present Continuous Tense Negative Sentences Examples
- She isn’t losing any weight in this health program.
- He is not riding a bike.
- You are not swimming in the sea.
- They are not going to school today.
- The number of uneducated people isn’t rising in Pakistan.
- They aren’t fightingfor human rights.
- They are not learning to handle their problems as a team.
- The children aren’t changing their attitude to studies.
Present Continuous Tense Interrogative Sentences with Examples
Invert the be verb (is, am, are) and the subject to form the interrogative sentences in the present continuous tense.
Structure: Is/am/are + Subject + (Verb1) +ing + Object
Present Continuous Tense Interrogative Sentences Examples
- Is she arriving tomorrow?
- Is it still raining outside?
- Am I studying English grammar?
- Are They playing cricket?
- Are you buying a new shirt?
- Is the hurricane coming for the ocean?
Interrogative sentences in the present continuous tense can also be formed with wh-questions. To create interrogative sentences, start with wh-words, i.e., who, which, when, etc., then add the auxiliary verb (is, am, are), then subject, then the main verb in the present participle form.
Present Continuous Tense Wh- Questions Examples
- What is she doing right now?
- When is he arriving?
- When are they going on a picnic this week?
- How are they studying?
- Where is he living?
- Why is he studying here?
- Why isn’t she doing her homework?
Present Continuous Tense Negative Interrogative Sentences
The negative interrogative is formed by inverting the auxiliary verb and the subject and then adding the word, not after the subject.
Structure: is/am/are + Subject + not + (Verb1) +ing + Object
Present Continuous Tense Negative Interrogative Sentences Examples
- Are you not studying anymore?
- The children want to play outside. Isn’t it raining?
- Why are they not coming today?
- Is she not preparing for her exam this week?
- Is he not washing the clothes?
Uses of Present Continuous Tense with Examples
Present continuous tense is used for an ongoing action at the time of speaking.
- They are playing cricket. (now, at the time of speaking)
- He is studying. (now)
- We are reading an article about machine learning.
Present continuous tense is also used for a temporary action that does not happen when someone speaks.
- He is arriving tomorrow.
- I am visiting his house tonight.
It is sometimes used for future action or a definite arrangement in the near future.
Examples
- He is arriving the following Monday. (This means his arrival is part of a fixed timetable in the near future; therefore, we use the present continuous tense for this action.)
- She is going to school tomorrow.
- He is going to go to New York the following Monday. (future simple tense)
- He is going to New York the following Monday. (present continuous)
- Is he doing anything tomorrow?
- I am seeing my friend tomorrow.
- I am not going on holiday tomorrow.
- They have arranged everything. They are spending the next summer holiday in London.
- Our school team is taking part in the cricket tournament next year.
Both sentences express a future plan. It should be noted that the present continuous tense isn’t used for all future actions; it can only be used for activities we have planned.
To emphasize an ongoing action, we often use time expressions like still, currently, at present, or presently, at the moment, while, and now. These expressions help to denote continuous present.
Examples
- He is having lunch now.
- I am studying mathematics at the moment.
Present Continuous or Present Simple Examples
Sometimes, we use either present simple or present continuous to describe something we regularly do at a specific time.
- She usually leaves the office early in the evening.
- She is leaving the office early in the evening.
Some verbs sometimes are not used in the continuous form; such verbs are called stative verbs.
Stative verbs include Verbs of perception, emotion, thinking Process, verbs showing Possession, etc.
We use present simple tense instead of present continuous tense for these verbs, even if the action is happening right now.
Read the following examples.
- He likes me.
- She does not hate him.
- I own this car.
- She wants to go home.
When the meaning is changed, the stative verbs are also used in continuous form as well. For example, the stative meaning of the verb “think” is believed.
Examples
- She thinks (believes) that mathematics is complicated for most learners.
- I think (believes) he will come late.
- The verb think may be used as an action verb.
Further Examples of Present Continuous Tense
- She is looking exhausted.
- We are living in the US.
- He isn’t playing the piano.
- They are learning English at school.
- Are the crops growing well?
- She is still talking to her friend on the phone.
- We aren’t working on the farm this morning.
- He is leaving tomorrow.
- The garden measures 200 square feet, but we are measuring it again to ensure.
- Why are you being so difficult?
- Why isn’t she doing her homework?
- When are they taking children to the zoo?
- We are building a new school.
Difference Between Present Simple and Present Continuous with Examples
The following examples describe the difference between the simple and present continuous tenses. Here, you’ll notice verbs that express actions can be used in simple and continuous forms.
- Ahmad plays the guitar.
- Ahmad is playing the guitar.
The first sentence states a general fact, i.e., Ahmad knows how to play the guitar, or he often plays the guitar. The second sentence describes what is happening right now.
- Your brother tells lies. (a general fact)
- Your brother is lying to me. (what he is doing now)
- I read every day.
- I am reading every day.
- It does not rain on the moon.
- It isn’t raining outside.
- He has two sisters.
- He is having a bath.
- She usually wears a black shirt.
- She is wearing a black shirt.
- I read novels every day.
- I am reading a novel right now.
- The baby looks/is looking ill.
